- Tomcat Ejb Container Tote
- Tomcat Ejb Container Tote
- Tomcat Ejb Container Tracking
- What Is Ejb
- Ejb Tutorial
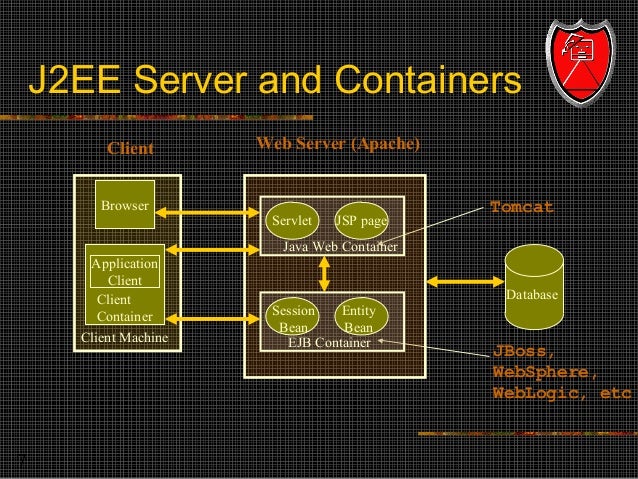
Apache Tomcat is an open source implementation of the Java Servlet and JavaServer Pages technologies. No, Tomcat does not support EJB. It is a Servlet/JSP container, not an EJB container. The Jakarta Project provides an implementation of the Servlets API called Tomcat, and an implementation of JavaServer Pages called Jasper. These are bundled together in the Tomcat release. However, the J2EE Reference Implementation, which supports EJB, is.
Enterprise Java beans – It is a server-based architecture, adhering to the specifications and requirements of the enterprise environment. The beans run in a container in four-tier architecture J2EE consisting of Client layer, Web layer, Application Layer, and Data layer. Difference between JB and EJB. EclipseLink JPA Deployed on Tomcat 6 using Eclipse WTP. Mediafire omnisphere 2 download. Tomcat 6 is not a Java EE 5 compliant server by design as it is a servlet container, however the servlet container is able to run EJB 3.0/JPA applications in application-managed Java SE (stand alone) mode.
Introduction
Tomcat is not a full-blown EE container so we must include some required libraries in order to enable CDI support. In this tutorial we will cover CDI configuration in Tomcat and also provide a working sample.
This tutorial considers the following software and environment:
- Ubuntu 12.04
- JDK 1.7.0.09
- Weld 1.1.10
- Tomcat 7.0.35
Configuration
Tomcat is not a full-blown EE container so we must include some required libraries in order to enable CDI support. In this tutorial we will be using Weld - the CDI reference implementation. The required Maven dependencies used in this tutorial are the following:
In order to enable CDI we must also place an empty beans.xml file in WEB-INF folder:

The last configuration step is to configure our CDI listener. We do this in web.xml:
The injected bean
Now let's define the bean that will be injected by CDI in our test servlet. Following is the bean interface:
Now the bean implementation:
A simple test servlet
Now let's define a simple servlet where we will inject our bean:
Note that the private property service is annotated with @Inject. This means that when the container is initializing the servlet it will look for a Service implementation. It will find our implementation - ServiceBean - and inject it into the servlet.
Tomcat Ejb Container Tote
When we deploy the application in Tomcat and access the servlet mapped URL we will get the following output:
Tomcat Ejb Container Tote
The tutorial source code is available for download at the end of this page.
Tomcat Ejb Container Tracking
Download source code from this article
What Is Ejb
Related Articles
Ejb Tutorial
Comments

Comments are closed.